Difference between HTTP and HTTPS ?
HTTP Stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol
it uses port: 80
HTTPS Stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure
it uses port: 443
In simple terminology:-
whenever you’re using a web browser like Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Opera to browse the internet via various protocols (Protocols are a set of rules) to access google.com from the browser we enter it on your URL filed it sends a request to the Google server on the internet, The request is passed through your browser to the server through various networks which are not in your control,
When a request made, it transfers from various networks by using HTTP Protocol it moves in plain text format where it is visible for the hackers, ISP, and criminals using different hacking tools they will know what your browsing and what your buying online and they can get your data like username, password, card details, etc while you’re using HTTP, So there is a threat to your privacy.
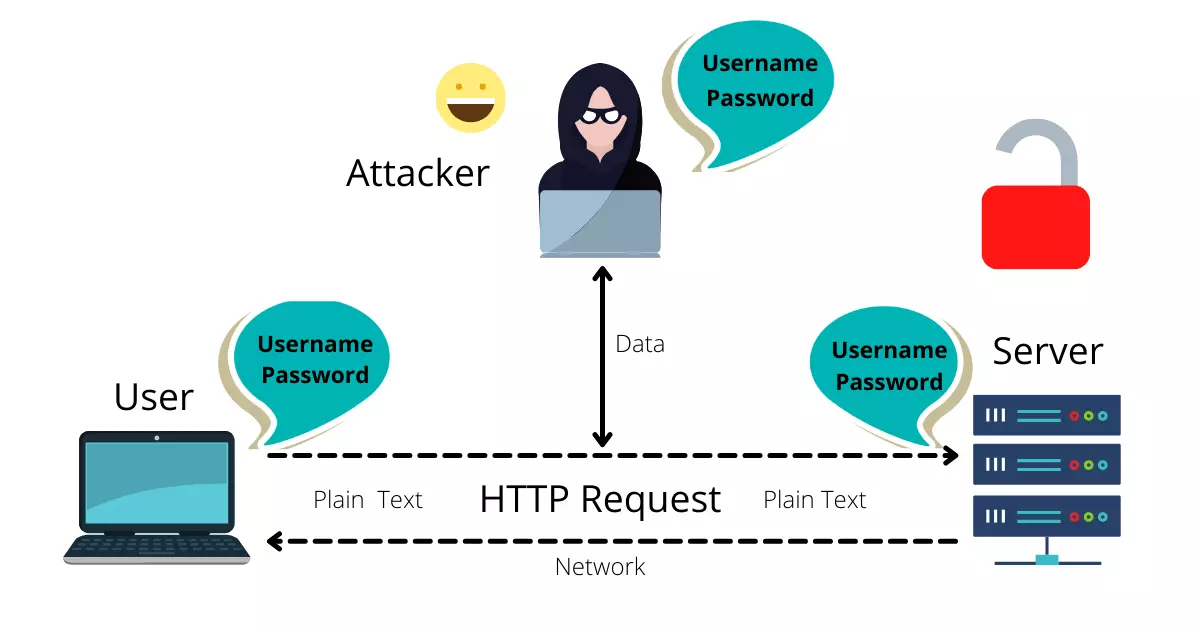
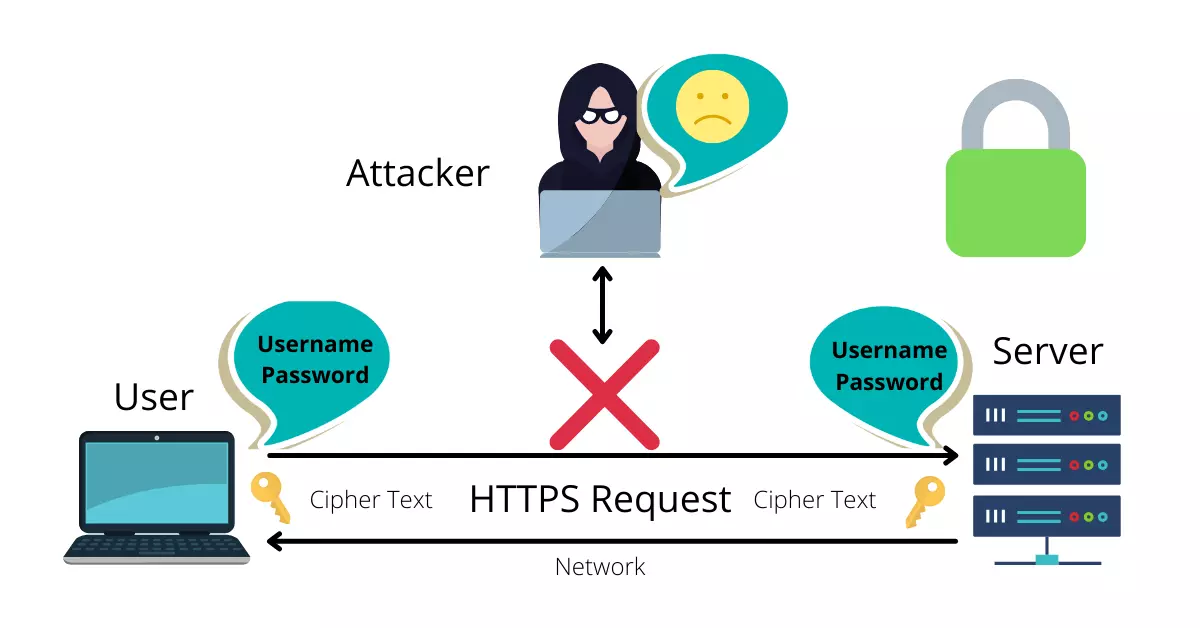
Then how to protect it? Here it comes the HTTPS
Where your request and data both transfers in an encrypted format (Cipher Text) where It can only decrypt by the server and your browser from both ends
plain text: abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
cipher text: phqgiumeaylnofdxjkrcvstzwb
Difference between HTTP and HTTPS in tabular form
| HTTP | HTTPS |
| HyperText Trasfer Protocol | HyperText Trasfer Protocol Secure |
| It uses port 80 | It uses port 443 |
| SSL not required | SSL required |
| Works at Application Later | Works at Transport Layer |
| Domain Validation Not required | The least Domain Validation required |
| In-secure data transfer | Secure data transfer |
| No Encryption of Data | Encryption of Data |
In Detail Technical information:-
It is for computer science and IT students and professionals, I hope you have basic knowledge of networking and cryptography of network security.
When an HTTP request is moving in a network, the devices connected to that network can access the HTTP request structure information like
- Request Line
- General Header
- Request Header
- Entity Header
- Body Message
Request Line: it consists of three
- A method like (GET, POST)
- Request URL ( Page link)
- Protocol Version ( HTTP/1.1)
General Header: it consists of
- Host ( Domain name www.google.com)
- Cache-Control
- Connection Type
Request Header: it consists of
- Content-Length
- Accepted Language
Entity Header: it consists of
- Content-Length
- Content-Language
Body Message: message or content
Any device connected to the network can access the data body message also using various attacks like Man in the middle attack or tools like Ettercap, Wireshark, (it is a tool for network protocol analysis)
To prevent this type of data breaches we use HTTPS, In that, we use standard cryptography techniques to encrypt and decrypt data from the client to the server it uses SSL/TLS ( Secure Sockets Layer ) ( Transport Layer Security)
How HTTPS works:
After installing the SSL Certificate and private key files in the webserver, the request comes from HTTPS port 443 key exchanges and authenticate the server and client connection it encrypts the content like text, images, documents, media, etc in that standard encryption method like RSA with different key digits like 128 or 256 digits nowadays 2048 bits are also available.
The Key exchange works when the request is going to a web server, the request is encrypted using a public key then only the webserver which having its private key can encrypt that message so the attacker can not decrypt that.
HTTPS uses both symmetric and asymmetric encryption based on the data or information to be transferred.
HTTPS protects your information on the internet when your browsing check the website either HTTP or HTTPS
To check the website SSL Certificate free of cost visit SSL Checker




Leave a Reply